Definition and Importance
Overview of Different Routes

Enteral Routes of Drug Administration
Oral Route
Sublingual and Buccal Routes

Parenteral Routes of Drug Administration
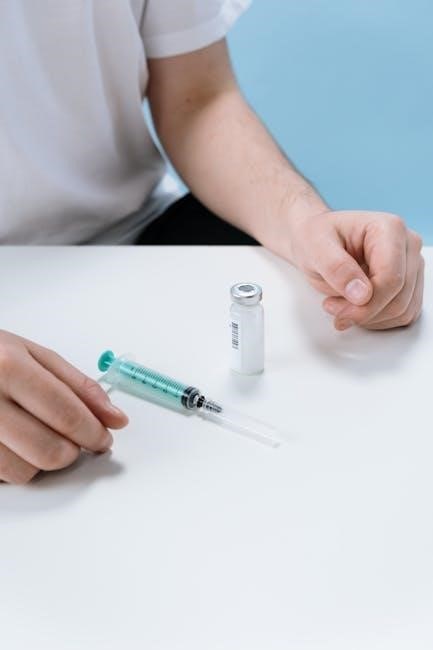
Intramuscular Route
The intramuscular route involves injecting a drug directly into a muscle, typically in the thigh, arm, or buttock, using a needle and syringe. This method allows for the drug to be absorbed into the bloodstream quickly, often producing rapid effects. The intramuscular route is commonly used for vaccinations, antibiotics, and other medications that require a rapid onset of action. The drug is injected into the muscle tissue, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream and distributed throughout the body. This route is often preferred for drugs that are not well absorbed when taken orally, or for patients who have difficulty swallowing or absorbing medications. The intramuscular route can be used for both short-term and long-term therapy, and is a common method of administration in clinical settings. Overall, the intramuscular route is an effective and efficient method of drug administration, offering a range of benefits and advantages for patients and healthcare providers.
Subcutaneous Route
The subcutaneous route involves injecting a drug into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin, using a small needle and syringe. This method is often used for medications that need to be administered over a long period, such as insulin or growth hormone. The subcutaneous route allows for slow and steady absorption of the drug into the bloodstream, providing a sustained release of the medication. This route is also commonly used for vaccinations, such as the influenza vaccine, and for medications that require frequent dosing, such as heparin. The subcutaneous route is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, with minimal risk of adverse reactions. The drug is injected into the subcutaneous tissue, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream and distributed throughout the body. This route is often preferred for patients who require frequent injections, as it is relatively painless and can be self-administered. Overall, the subcutaneous route is a convenient and effective method of drug administration.
